The pyspark.sql.functions.lag() is a window function that returns the value that is offset rows before the current row, and defaults if there are less than offset rows before the current row. This is equivalent to the LAG function in SQL. The PySpark Window functions operate on a group of rows (like frame, partition) and return a single value for every input row
Key Points of Lag Function
- lag() function is a window function that is defined in
pyspark.sql.functions.lag()which is equivalent to SQL LAG. - In order to use this function first you need to partition the DataFrame by using pyspark.sql.window.
- It returns the value that is offset rows before the current row, and defaults if there are less than offset rows before the current row.
- An offset of one will return the previous row at any given point in the window partition.
- It returns null for top rows or first rows.
- It is a useful function in comparing the current row value from the previous row value.
1. Syntax of lag() Function
Following is the syntax of PySpark lag() function.
# lag() Syntax
pyspark.sql.functions.lag(col, offset=1, default=None)
col– Column name or string expression. Column or stroffset– Value should be an integer when present. The number of rows back from the current row from which to obtain a value. If not specified, the default is 1.default– Default value to be used for a null value.
2. PySpark lag() Function Usage with Example
For example, an offset of one will return the previous row at any given point in the window partition.
It works similar to a PySpark lead() function where we access subsequent rows, but in lag function, we access previous rows. It is a useful function in comparing the current row value from the previous row value.
First, let’s create the PySpark DataFrame.
# Imports
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Create SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName('SparkByExamples.com') \
.getOrCreate()
# prepare Data
simpleData = (("James", "Sales", 3000), \
("Michael", "Sales", 4600), \
("Robert", "Sales", 4100), \
("Maria", "Finance", 3000), \
("James", "Sales", 3000), \
("Scott", "Finance", 3300), \
("Jen", "Finance", 3900), \
("Jeff", "Marketing", 3000), \
("Kumar", "Marketing", 2000),\
("Saif", "Sales", 4100) \
)
columns= ["employee_name", "department", "salary"]
# Create DataFrame
df = spark.createDataFrame(data = simpleData, schema = columns)
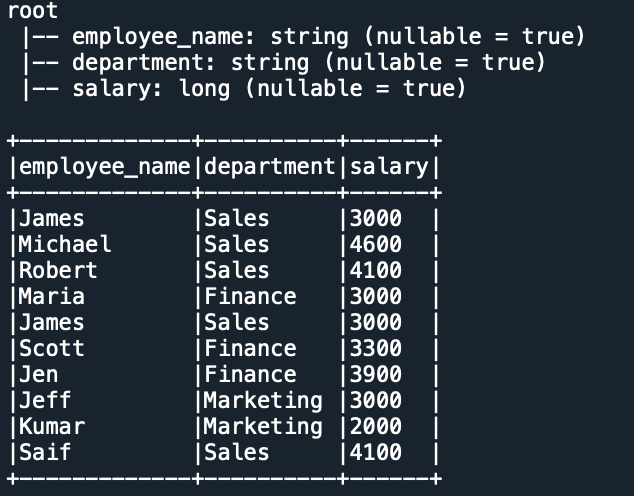
df.printSchema()
df.show(truncate=False)
Yields the below output.
Since the lag() is a window function, we need to group the rows like frame or partition using window.partitionBy(). In the below example I am grouping the rows on department column and sorting by salary column.
# Create window
from pyspark.sql.window import Window
windowSpec = Window.partitionBy("department").orderBy("salary")
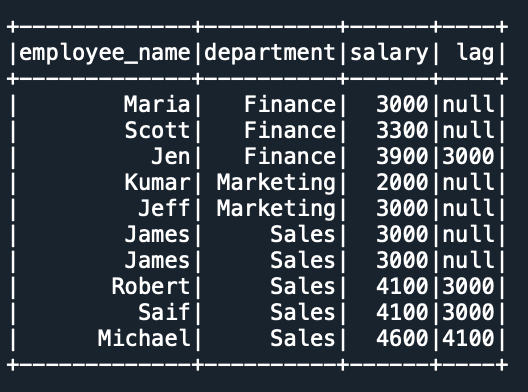
Once we have the window defined, lets use lag() on salary column with offset 2. withColumn() adds a new column named lag to the DataFrame.
# Using lag function
from pyspark.sql.functions import lag
df.withColumn("lag",lag("salary",2).over(windowSpec)) \
.show()
Yields the below output. Note that the first 2 rows has assigned null for each partition/group as we have offset 2.
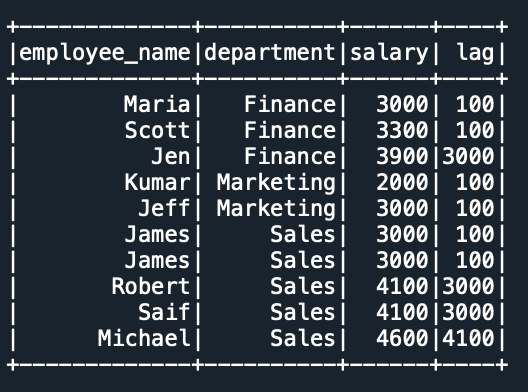
PySpark lag() Example with Default Value
You can use the default param to set the default value for null values. When you use this, all null values are replaced with the specified value.
# Using lag function with default
from pyspark.sql.functions import lag
df.withColumn("lag",lag("salary",2,default=100).over(windowSpec)) \
.show()
Yields the below output.
Complete Example
Following is the complete example of the PySpark lag() function.
# Imports
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Create SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName('SparkByExamples.com') \
.getOrCreate()
# prepare Data
simpleData = (("James", "Sales", 3000), \
("Michael", "Sales", 4600), \
("Robert", "Sales", 4100), \
("Maria", "Finance", 3000), \
("James", "Sales", 3000), \
("Scott", "Finance", 3300), \
("Jen", "Finance", 3900), \
("Jeff", "Marketing", 3000), \
("Kumar", "Marketing", 2000),\
("Saif", "Sales", 4100) \
)
columns= ["employee_name", "department", "salary"]
# Create DataFrame
df = spark.createDataFrame(data = simpleData, schema = columns)
df.printSchema()
df.show(truncate=False)
# Create window
from pyspark.sql.window import Window
windowSpec = Window.partitionBy("department").orderBy("salary")
# Using log function
from pyspark.sql.functions import lag
df.withColumn("lag",lag("salary",2).over(windowSpec)) \
.show()
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned the syntax of lag() function and learned it is a window function that returns the value that is offset rows before the current row, and defaults if there are less than offset rows before the current row
Related Articles
- PySpark Broadcast Variable
- PySpark Broadcast Join with Example
- PySpark Random Sample with Example
- PySpark reduceByKey usage with example
- Pyspark – Get substring() from a column
- Show First Top N Rows in Spark | PySpark
- PySpark Create DataFrame from List
- PySpark Concatenate Columns
- PySpark Refer Column Name With Dot (.)
